Water Testing
 If your home, or a home you may purchase, has a private well as its water source, it is not regulated by local or state regulations in Massachusetts. The EPA recommends testing annually for the most common contaminants.
If your home, or a home you may purchase, has a private well as its water source, it is not regulated by local or state regulations in Massachusetts. The EPA recommends testing annually for the most common contaminants.
You may also consider testing if:
- You notice a color, odor or poor taste to your water
- You notice sediment, staining, residue or extensive corrosion
- You or a family member have frequent gastro-intestinal upset
- Your household plumbing contains lead
- Your well “runs dry” or experiences low pressure/yield
- You plan on purchasing or selling a home
Basic Profile
Our Basic Profile checks for common contaminants and is our most requested test. Included: coliform*, nitrate, nitrite, sodium, chloride, manganese, iron, hardness, turbidity, pH, sulfate, color, odor and chlorine.You can add any individual test to this, including radon.
Note: The Basic Profile does not satisfy the Town of Hopkinton’s requirements for real estate transactions.
Hopkinton Well Profile
The town of Hopkinton, MA Board of Health has specific water quality testing requirements for the transfer of any property that has a private well as its water source. Our Hopkinton Well Profile meets these requirements. Upon completion we provide the homeowner and the Board of Health with a completed report. The Hopkinton Well Profile includes: coliform*, volatile organic compounds, lead, arsenic, cadmium, mercury, iron, manganese, ammonia, nitrate, nitrite, alkalinity, hardness, sodium, chlorides, pH, color, odor and turbidity.Individual Tests
Any component of the bundled profiles along with dozens of other individual tests can be performed as a singular test or we can build a bundled profile for your specific need. Call or email with your specific need so we can discuss.*In addition to the testing mentioned above, Able Septic can assist homeowners with chlorinating their well should any testing reveal coliform contamination. Chlorination is generally effective in resolving a positive coliform result. Any other mitigation needed we are happy to work with homeowners to assist them in finding the right professional for the job.
Radon
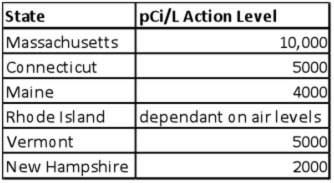
Radon is a colorless, tasteless, odorless, radioactive gas that can contribute to lung cancer. The breakdown of naturally occurring uranium in our environment generates radon and it can invade our water supplies, including private wells. Radon in water becomes problematic when steam from water is inhaled, such in a hot shower or from a dish washer. “Pockets” of uranium underground effect all wells differently depending on how close to a well they are. Your well and your neighbor’s well may have very different levels of radon. There is currently no universally acceptable level for radon in water, though some individual states have set limits, and they vary widely. A national guideline is being considered.Current Massachusetts state guidelines recommend a mitigation system for your well if the radon in your water is 10,000 pCi/L or higher. However, other New England states have very different recommendations: